Timer 0 in the ATmega8 microcontroller is a fundamental tool for those diving into the world of embedded systems. As one of the three timers available in this popular AVR family microcontroller, understanding Timer 0 is crucial for a plethora of applications.
update
Timer 0 in the ATmega8 is an 8-bit timer, meaning it can count from 0 to 255. Once it reaches its maximum value, it overflows and starts again from zero. This simple yet powerful tool allows developers to create precise time intervals and delays in their applications.
The counting direction is always up (incrementing), and no counter-clear is performed. The counter simply overruns when it passes its maximum 8-bit value (MAX = 0xFF) and then restarts from the bottom (0x00).
In normal operation, the Timer/Counter Overflow Flag (TOV0) will be set in the same timer clock cycle as the TCNT0 becomes zero. The TOV0 Flag in this case behaves like a ninth bit, except that it is only set, not cleared.
However, combined with the timer overflow interrupt that automatically clears the TOV0 Flag, the timer resolution can be increased by software. A new counter value can be written anytime.
![]() A simplified block diagram of the 8-bit Timer/Counter
A simplified block diagram of the 8-bit Timer/Counter
The Timer/Counter can be clocked internally or via the prescaler, or by an external clock source on the T0 pin. The Clock Select logic block controls which clock source and edge the Timer/Counter uses to increment its value. The Timer/Counter is inactive when no clock source is selected. The output from the clock select logic is referred to as the timer clock (clkT0).
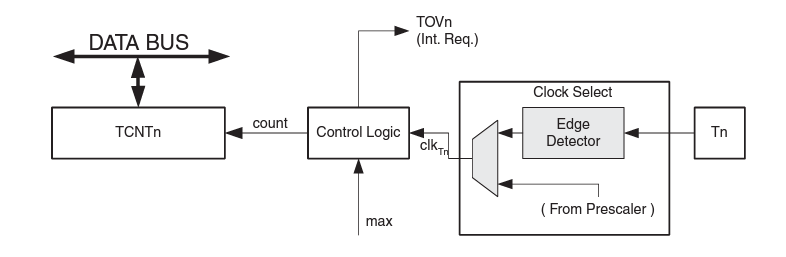 Timer/Counter Unit Block Diagram
Timer/Counter Unit Block Diagram
The Timer/Counter can be clocked by an internal or an external clock source. The clock source is selected by the clock select logic which is controlled by the clock select (CS02:0) bits located in the Timer/Counter Control Register (TCCR0).